Abstract
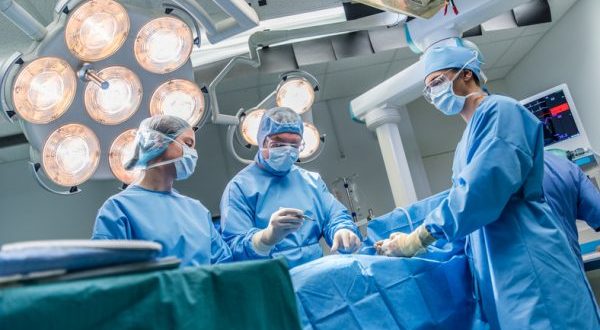
Due to their many benefits, laparoscopic surgical procedures have become increasingly popular in the operating theaters over the last few years. Virtual reality training simulators played a significant role during this transition from conventional procedures to laparoscopic procedures by improving surgical skills such as hand-eye coordination in laparoscopy, and practicing surgical cases that cannot be easily created using models physical. This paper presents a general framework for such a training simulator and at the same time identifying its main components and enhancing its specific roles in different laparoscopic skills. The paper also describes a laparoscopic simulator, developed in our laboratory, based on the proposed framework. The results are promising and they open new doors for research and development.
Click here: Laparoscopic Surgery Simulator
Introduction
For sophisticated training, from jet-fighting to project management, virtual reality simulators (VR) play an important role in the trainee’s learning. Laparoscopy, which is a type of minimal invasive surgery (MIS) that allows endoscopy and other instruments to be inserted into the body of the patients through small holes and working on the patient using screen output from the endoscope, is no exception. VR simulators facilitate the coordination of lacoscopy eyes, depth understanding, the ability to operate within a limited space and control the ability of non-intuitive motion instruments. Similarly, when the surgical robots were introduced, it was more important to train the surgeons to use such robots correctly. Due to the high cost of commercially available surgical robots, VR simulators provide an economically more viable option for the provision of robotic surgical training. In addition, a surgical simulator is a safer option than practice on living patients and provides better training because the body tissue properties are more similar in simulators.
The number of commercial surgical simulators, including and, 4 are in use in surgical training institutions. is a simulator for surgical system with a console master similar. In contrast, speed is based on the speed levers to control the virtual surgical instruments. Similarly, various simulators are commercially available to learn the traditional laparoscopic surgery. Commonly used ones are.
However, these simulators are available on a commercially expensive basis. Surgical simulators are the most commonly used insulators, but they say that “inadequate laparoscopic surgical simulators involve surgical training”. According to our analysis, this is mainly due to the high cost of laparoscopic simulators. Therefore, the problem can be solved if a state-of-the-art Surgical Simulator is available at a lower cost. The availability of such a simulator would facilitate the introduction of laparoscopic surgeries in developing countries and thus allow them to reduce their healthcare burden. There is an abundance of laparoscopic simulators available which are free but do not train up to the mark. For example, videos can be accessed even when one laparoscopic simulator is made at home. laparoscopic surgeon needs. The proposed framework can be used as a benchmark for assessing the effectiveness of a laparoscopic cost-effective simulator and therefore a judgment on whether the necessary training requirements can be met.
Proposed Framework
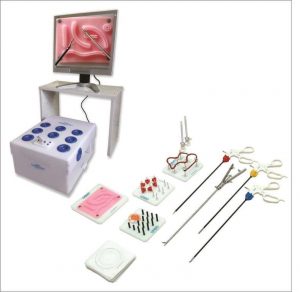
A laparoscopic simulator consists mainly of three main modules: A mechanical interface, a and a software application.
The mechanical interface allows the user to interact with the Simulator software application. For ordinary laparoscopic training simulators, such as, the mechanical interface is designed to imitate the actual laparoscopic tool in structure and functionality. In the case of a laparoscopic robotic trainer, the mechanical interface should replicate the actual surgical robot handlers, such that the users can get the same feeling as a real surgery during the training process.
The controller circuit is usually invisible and consists of sophisticated electrical components that are responsible for the interaction and communication between the mechanical interface and the software application. Primarily, the controller circuit is composed of flags smart, which are placed on the mechanical interface sections to measure the mechanical movements. These movements are then transferred to the computer to handle the software application.
For more information visit our website Laparoscopic Surgery Simulator
 Universal Bloggers
Universal Bloggers